Russia’s Offer to Build an SMR in Kyrgyzstan and its Implications
By Sergey Sukhankin
In late 2025, during his visit to Kyrgyzstan, Russia’s President Vladimir Putin declared Russia’s readiness to build a small modular nuclear power reactor (SMR) in Kyrgyzstan, thereby signaling Moscow’s intention to move beyond traditional trade relations toward projects in long-term strategic infrastructure. Russia’s proposal may be justified by the need to address Kyrgyzstan’s persistent problem of frequent energy shortages, caused by rising consumption, aging energy infrastructure, and overreliance on hydropower as the primary source of electricity generation. At a deeper level, however, the initiative reflects Moscow’s post-2022 strategy, premised on exporting high-technology solutions to politically friendly states and anchoring influence through capital-intensive projects with multi-decade life cycles, such as SMRs. Undoubtedly, if successfully constructed, an SMR could strengthen Kyrgyzstan’s energy security. Yet, it would also exacerbate the country’s strategic dependence on Russia by locking it into long-term technological, financial, and regulatory reliance, rendering the project arguably more geopolitical in nature than economic.

BACKGROUND:
Kyrgyzstan’s energy system has long suffered from structural fragility stemming from the country’s overarching dependence on hydropower: more than 90 percent of electricity generation derives from this source, largely produced by the Toktogul cascade. Exposed to multiple risks and weaknesses, such as droughts, aging Soviet-era infrastructure, and rapidly growing domestic demand, the system has shifted from experiencing occasional electricity deficits to facing a structural crisis. In 2023, the government introduced a state of emergency in the energy sector, explicitly acknowledging the inability of existing generation capacity and demand-management tools to ensure uninterrupted supply. Experts note that persistent electricity shortages could further undermine Kyrgyzstan’s socio-economic stability and, in the longer term, generate political repercussions posing serious challenges to the country’s leadership. Nevertheless, Kyrgyzstan appears unable to address this challenge independently. Beyond economic constraints, particularly the high fixed costs associated with hydropower generation, recent water shortages have further exacerbated the problem. In this context, Kyrgyz authorities have expressed interest in developing nuclear energy projects, with external financial support, as a potential solution to the country’s long-term electricity supply challenges.
This interest emerged in parallel with Russia’s broader strategic effort to diversify its export portfolio beyond raw materials. In this context, Moscow has actively promoted the deployment of an SMR in Kyrgyzstan as part of a wider push to export high-value energy technologies. The origins of this initiative can be traced to early 2022, when Rosatom, Russia’s state-owned nuclear corporation, and the Kyrgyz Ministry of Energy signed a non-binding memorandum on cooperation in the peaceful use of nuclear energy. Beyond signaling technical cooperation, the memorandum laid the groundwork for potential SMR construction and the gradual development of a national regulatory framework, indicating a long-term and structurally embedded approach rather than a short-term energy solution. Following the outbreak of war between Russia and Ukraine in February 2022 and Russia’s exposure to an expanding array of international (Western) sanctions, the idea gained renewed momentum.
Given Kyrgyzstan’s highly specific socio-political environment, distinct from that of other Central Asian states, public opinion on nuclear energy is an issue the ruling elite cannot afford to ignore. Available evidence suggests that societal attitudes toward nuclear power remain ambivalent. According to public opinion surveys conducted in 2024, 58 percent of respondents expressed support for the development of nuclear energy, while 38 percent voiced categorical opposition. Support is largely driven by expectations that nuclear power could help meet the country’s growing electricity demand and create new employment opportunities. At the same time, significant concerns persist regarding nuclear safety, environmental risks, seismic vulnerability, and the state’s institutional capacity to regulate complex and high-risk technologies. As a result, nuclear energy remains a politically sensitive and potentially contentious issue within Kyrgyzstan’s domestic political landscape.
IMPLICATIONS:
Should the Kyrgyz political leadership respond positively to Russia’s proposal, the country would face a combination of potential benefits and risks, which can be broadly categorized as follows.
First, meeting energy needs and ensuring system stability. From an energy-security perspective, the emergence of an SMR could positively affect Kyrgyzstan’s electricity balance. Unlike hydropower, nuclear generation provides continuous baseload output independent of seasonal water availability. Russian officials have indicated that Kyrgyzstan could be offered a plant based on the RITM-200N reactor design, with total capacity ranging from approximately 110 to 440 MW, depending on configuration. This output could supply electricity to between 66,000 and 352,000 households simultaneously. Even at the lower end of this range, such capacity could reduce imports and ease pressure on hydropower assets during dry periods. That said, to fully realize these benefits, Kyrgyzstan would need to meet several conditions: the establishment of a comprehensive regulatory framework, an independent nuclear safety authority, trained operators, emergency-response systems, and long-term arrangements for fuel supply and waste management. For Kyrgyzstan, this would entail either creating much of this infrastructure from scratch or delegating these functions to Russia, a choice that would inevitably deepen institutional dependence on Russia.
Second, the issue of economic costs and long-term dependence. Although SMRs are often presented as cheaper and more flexible than conventional large nuclear plants, they remain capital-intensive projects with long payback periods. In practice, this would require Kyrgyzstan to assume long-term financial obligations while ceding significant control over critical components of its energy system to a foreign state with a documented record of using energy as a geopolitical instrument of pressure. Moreover, dependence would extend well beyond construction, encompassing fuel supply, maintenance, software, spare parts, and periodic upgrades. For Kyrgyzstan, this would narrow future strategic options and increase the cost of diversifying away from Russian technology for decades to come.
Third, implications for domestic politics. Nuclear projects frequently face public resistance even in countries with strong institutions. In Kyrgyzstan, where trust in state decision-making is limited and political competition is intense, an SMR could become a focal point for opposition mobilization, particularly in the event of an incident or if Russia were perceived as leveraging Kyrgyzstan’s dependence. Without transparent consultations, credible safety assurances, and clearly articulated local benefits, the project risks appearing as an externally imposed geopolitical arrangement rather than a sovereign national development choice.
Fourth, intra-regional geopolitical effects. The Central Asian “water–energy–food” nexus is inherently conflict-prone due to divergent seasonal priorities: upstream states, particularly Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan, seek to maximize winter electricity generation, while downstream countries depend on summer water flows for irrigation. From a policy perspective, the deployment of an SMR could offer a structural advantage by providing reliable winter baseload generation, thereby reducing reliance on hydropower and creating space for more predictable and cooperative water–energy arrangements with Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan. However, this opportunity entails significant trade-offs. An SMR would deepen long-term technological and financial commitments to an external partner and could become entangled in regional and extra-regional geopolitical bargaining. If politicized, the project risks undermining trust, constraining policy flexibility, and further securitizing energy governance in Central Asia rather than contributing to its stabilization.
CONCLUSIONS:
Russia’s proposal to build an SMR in Kyrgyzstan represents a pivotal choice that extends well beyond energy policy. While the project could substantially enhance electricity security and reduce vulnerability to hydrological shocks, it would also bind Kyrgyzstan to long-term technological, financial, and regulatory dependence on Russia. In a politically pluralistic and socially sensitive environment, such dependence entails significant domestic and regional risks. Ultimately, the project’s impact will depend on whether Kyrgyz authorities can balance short-term energy gains against strategic autonomy, address public concerns transparently, and prevent the SMR from becoming an instrument of geopolitical leverage rather than a catalyst for sustainable development.
AUTHOR’S BIO: Dr. Sergey Sukhankin is a Senior Fellow at the Jamestown Foundation and the Saratoga Foundation (both Washington DC) and a Fellow at the North American and Arctic Defence and Security Network (Canada). He teaches international business at MacEwan School of Business (Edmonton, Canada). Currently he is a postdoctoral fellow at the Canadian Maritime Security Network (CMSN).
The Strategic Dilemma of Secondary Sanctions in Central Asia and the South Caucasus
By Charlotte Krausz
President Trump's recent imposition of 25 percent tariffs on India for importing Russian oil signals a potential expansion of secondary sanctions to other Russian energy customers. The policy shift threatens to extend punitive measures to post-Soviet states in Central Asia and the South Caucasus that remain heavily dependent on Russian energy infrastructure. While aimed at curtailing Russia's war revenues, such measures could paradoxically drive these strategically important regions closer to Moscow's orbit, undermining years of U.S. and EU engagement in the region.

BACKGROUND: In his statements, Trump has criticized countries that import oil and accused them of funding the “Russian war machine.” By stopping Russia’s revenues from its largely petrostate-based war economy, the U.S. seeks to thwart Russian advances in Ukraine and punish Putin. Yet imposing high tariffs on countries dependent on Russia for their energy supply, especially on post-Soviet states in Central Asia and the South Caucasus, could have far worse ramifications for U.S. and EU aspirations in the region and drive former Soviet republics closer to Russia once more
A key example of this policy shift occurred in the first days of August 2025, when President Trump imposed a 25 percent tariff (later raised to 50 percent) on India for being a major buyer of Russian oil. Randhir Jaiswal, a spokesman for the Foreign Ministry of India, said that “the targeting of India is unjustified and unreasonable.” Given that India buys one-third of its crude oil from Russia, India is unlikely to change course, and the tariffs have badly damaged relations with India. The move is especially surprising given Trump’s past cordial relationship with Modi and the Biden administration's geopolitical courting of India. Biden even hosted Modi for a state dinner in June 2023.
In a recent opinion piece in The Washington Post, Andriy Yermak, Ukraine’s chief of the presidential office, praised the high tariffs on India. Yermak declared that it was a “great first step” but called for more pressure and for a “full economic blockade” of Russia. While Ukraine understandably wants everything possible to be done to end the war and bring peace, not all avenues will lead to the desired outcome. The decision for Europe to get off Russian oil following the full-scale invasion of Ukraine in 2022 was apparent and necessary. And though it led to an increase in energy costs and inflation, alternative energy sources were found, and Russia lost a vital stream of revenue. The expansion of these sanctions, this reasoning goes, will help the war effort and thwart Russia’s imperial ambitions.
But this strategy could be disastrous if poorly applied, especially in Central Asia and the South Caucasus, where countries are still dependent on Russia for energy needs. The energy landscape in Central Asia reflects decades of Soviet-era infrastructure and integration. Central Asian countries, except oil-rich Turkmenistan, remain highly reliant on Russian energy infrastructure and benefit from shared Soviet-era energy grids and the Eurasian Economic Union.
The South Caucasus presents a similar case. Georgia and Armenia, even more so, are largely dependent on Russian oil and have limited energy supply options. Georgia lacks domestic oil refineries and imports primarily from Russia and Azerbaijan, with Russian imports recently surpassing Azerbaijani supplies for the first time in eighteen years despite troubled bilateral relations. Armenia faces even greater constraints, with Gazprom maintaining a monopoly over natural gas imports and distribution. Natural gas made up 80 percent of Armenia’s energy imports in 2020. The rest comes from Iran in an electricity-for-natural trade deal. Armenia’s natural gas imports are delivered through the North-South Gas Pipeline via Georgia. Other regional pipelines bypass Armenia due to geopolitical conflicts with Azerbaijan and Turkey.
IMPLICATIONS: Following the closure of European markets to Russian oil after the 2022 invasion of Ukraine, Russian energy companies redirected their focus towards Central Asia, leading to an increase in Russian energy imports into the region. Russia and Central Asian countries rely on the same Soviet-era-built energy grid and EAEU membership. Russian investment in Central Asia’s energy infrastructure has expanded since 2022, including nuclear power plants in Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan and hydroelectric facilities elsewhere. Even Kyrgyzstan, despite being a renewable energy leader, plans to double its Russian oil imports by 2040.
Despite their energy dependence on Russia, both Armenia and Georgia have sought EU membership in the past. Both countries have undergone democratic revolutions, although their current political situations are tenuous. After Russia failed to defend Armenia from Azerbaijan’s September 2023 offensive, public opinion of Russia dramatically decreased, with two-thirds expressing a negative view and 40 percent viewing Russia as a threat. When the Georgian government withdrew from EU accession in November 2024, protests lasted for months demanding a reversal. Armenia and Georgia also share ties to Europe and the U.S. in terms of tourism, culture, and ethnic diasporas.
The U.S. imposing sanctions or high tariffs on countries in Central Asia and the Caucasus has the potential to undo decades of U.S. outreach to these regions. These could not separate their energy supplies from Russia without great harm to their own economies, nor would such a tradeoff be worth it to them. Antagonist trade policies would increase anti-American sentiment, inhibit future American investment, and thrust these post-Soviet states back into Moscow’s orbit.
Secondary sanctions on Russian oil importers are not assured to change the situation on the ground in Ukraine, which has been at a territorial standstill for months. Russia has proved more than capable of keeping its war machine growing and expanding under international sanctions. These approaches are less effective than simply supplying Ukraine directly with the weapons it needs to liberate territory and defend its skies.
Should the U.S. see strategic importance in weaning post-Soviet republics off Russian oil, it could encourage alternative energy routes and the use of renewable energy. Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan are already at the forefront in renewables like wind and hydroelectric power. A key alternative route could source energy from Turkmenistan. Turkmenistan has the fourth-largest natural gas reserves in the world. As Michael Doran from the Hudson Institute explains, “We just need a few kilometers of pipeline to be built in order to connect up Turkmen gas to Azerbaijan, which can then flow comfortably to Europe across Georgia … Turkmen Gas could end the dependence of Europe on Russian gas.” In addition, the U.S.-brokered peace treaty between Armenia and Azerbaijan presents new energy options for Armenia. If Armenia’s borders with Azerbaijan and Turkey were to be opened, it could diversify its energy imports rather than remaining reliant on Russia.
CONCLUSIONS: Post-Soviet states in Central Asia and the Caucasus are caught between a revanchist Russia and growing ties with the West. Central Asia and the South Caucasus have much to offer the West, from energy deposits to critical minerals, emerging democracies, and tourism. A “full economic blockade” would not only be impossible to enforce but also detrimental to long-term U.S. interests.
The countries of the Central Asia and Caucasus regions are aware of the great power rivalries surrounding them. They understand their precarious situations and the importance of not antagonizing Russia. If the U.S. wants to have a presence in Central Asia and the South Caucasus in the decades to come, it must respect the inherent multilateralism of these regions. As the war in Ukraine drags on, Washington must decide to what extent it sees importance in stopping the flow of Russian oil. It must weigh the value of cutting Russian oil revenues against future relations with post-Soviet countries.
AUTHOR’S BIO: Charlotte Krausz is a researcher at the American Foreign Policy Council, a Washington-based think tank. She is an undergraduate at the University of St. Andrews studying International Relations and Persian.
The Middle Corridor and the Russia-Ukraine War: the Rise of New Regional Collaboration in Eurasia?
By Selçuk Çolakoğlu
January 31, 2023
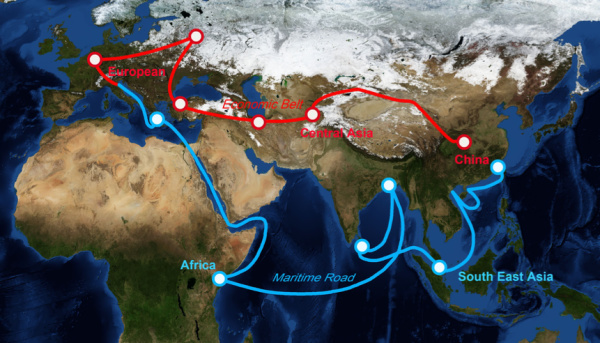
After Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, the West‑led sanctions regime against Russia, coupled with Russian counter-sanctions, has affected everything from energy resources and logistics to banking transactions and customs procedures. Western countries have realized that Moscow can weaponize its geopolitical position and logistic networks. Strategic over‑dependence on Russia’s energy, markets, and logistics has created significant challenges to neighboring countries due to increasing political tensions between the West and Russia. This development is undermining the Northern (Russian) Corridor’s position as the main overland East-West corridor. In turn, the alternative Middle Corridor is currently facing its best opportunity ever to take a leading position in connecting Europe and Asia.
Did Cryptocurrency Miners Crash the Central Asian Power Grid?
By Tony Pizur
February 22, 2022, the CACI Analyst
On January 25, Kazakhstan experienced widespread power outages that also affected neighboring Uzbekistan and Kyrgyzstan. Decaying infrastructure and increasing energy demand from cryptocurrency miners were blamed for the failure. Crypto operations are controversial because they divert scarce electricity resources from traditional household and industrial uses. After China’s complete ban on cryptocurrency activity last year, Kazakhstan was unprepared to accommodate the sudden influx of displaced crypto miners; nevertheless, the country quickly became the world’s second-largest source for newly minted bitcoins. Stopgap measures to restore power included patching physical infrastructure, sourcing electricity from Russia, and temporarily banning cryptocurrency mining.

Thinking Big About Caspian Energy
By Stephen Blank
November 29, 2018, the CACI Analyst
The signing of the Caspian convention in August 2018 has opened up exciting new possibilities for getting Central Asian oil and gas to European and global markets. The long-desired Southern Gas Corridor (SGC) from both shores of the Caspian has thus become a possibility. By thinking big, we can use Caspian gas for beneficial economic and political purposes. Whatever route Caspian energy takes to Europe, it must traverse the Caucasus and can be of substantial value in transforming the Eurasian geopolitical scene and agenda. Specifically, those parties who have the most to gain form resolving the Nagorno-Karabakh conflict can now devise a peace program that incorporates the use of energy to help foster an enduring peace between Armenia and Azerbaijan, reduce Russia’s ability to manipulate this conflict, and at the same time enrich them both as well as European consumers.





